In early 2018, Polaris Wireless participated in the CTIA’s Test Bed LLC Stage Zindependent vertical location testing in San Francisco, Atlanta and Chicago.
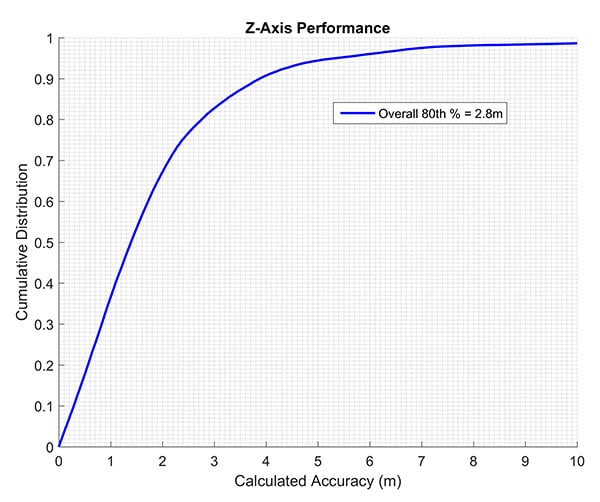
The company states that by using actual test call data to emulate active sensor compensation, its solution improved from 4.8- to 2.8-meter accuracy at the 80th percentile, which exceeds the commonly accepted definition of floor-level accuracy of under 3 meters.
The testing focus was to evaluate barometric-based solutions in advance of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) establishing a vertical location accuracy metric for compliance by wireless carriers in the Top 50 markets, beginning in 2021.
Polaris Wireless was one of two technology vendors selected to participate and was the only solution tested in all buildings in all three cities: 48 buildings, 312 test locations and 55,592 test calls. The Polaris Wireless test included the widest variety of device and barometric sensor manufacturers.
Polaris Wireless achieved an official Stage Z vertical accuracy of 4.8 meters, 80th percentile, with a minimal one-time compensation of the barometric sensor outside of the test cities. However, this one-time compensation did not present a true test of Polaris Wireless vertical location accuracy.
Barometric sensor compensation is arguably the leading source of error in vertical location determination. During the test, Polaris Wireless did not enable active, in-market compensation of the baro sensor and instead relied solely on just a few test calls outside of the test market.
After learning that the other vendor included active, in-market compensation, Polaris Wireless submitted a comparable set of results using the same methodology to the CTIA for consideration in the report. This data was drawn exclusively from actual test calls, in the period before final results were published, to emulate the original performance as if active compensation had been activated.
These are referred to as “limited active compensation” results because sensor bias estimates were updated monthly instead of in real time. The figure shows the increase in Polaris accuracy when allowing for this active compensation.
Polaris Wireless says it continues to improve on its three-dimensional accuracy for both public safety and commercial applications, and is exploring additional forums for independent performance evaluation.
https://www.gpsworld.com/polaris-wireless-achieves-floor-level-accuracy/